Fiber Fantastic: Your New Dietary Superstar
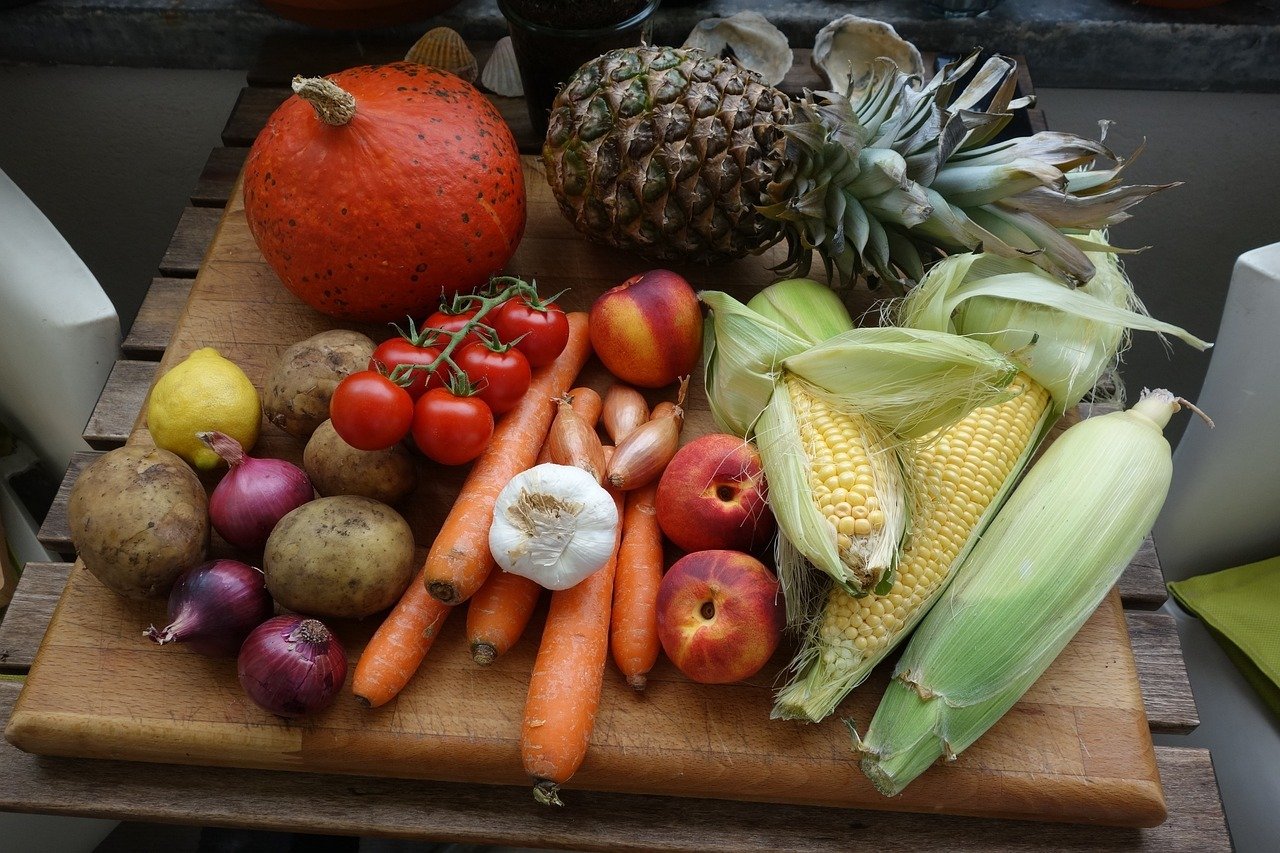

Table of Contents
- The Benefits of Fiber:
- – Promotes Digestive Health
- – Aids in Weight Management
- – Reduces Cholesterol Levels
- – Regulates Blood Sugar
- Top Fiber-Rich Foods:
- – Whole Grains and Cereals
- – Legumes and Beans
- – Fruits and Vegetables
- – Nuts and Seeds
- Incorporating Fiber into Your Diet:
- – Gradually Increase Intake
- – Choose Whole Foods
- – Experiment with New Recipes
- – Stay Hydrated
- Fiber and Gut Health:
- – Supports Healthy Gut Bacteria
- – Prevents Constipation
- – Reduces the Risk of Colon Cancer
- – Improves Overall Digestion
- Tips for a Fiber-Rich Lifestyle:
- – Read Food Labels
- – Plan Balanced Meals
- – Snack on Fiber-Rich Foods
- – Stay Consistent and Patient
The Benefits of Fiber:
Fiber is often referred to as the unsung hero of a healthy diet. It is a type of carbohydrate that is not broken down by our bodies, but instead passes through the digestive system intact. Although it doesn’t provide any nutrients or calories, fiber offers a multitude of benefits for our overall health and well-being.
Here are some of the incredible benefits of including fiber in your diet:
- Improved Digestive Health: Fiber adds bulk to your stool, making it easier to pass through the intestines and preventing constipation. It also promotes regular bowel movements and reduces the risk of developing hemorrhoids and diverticular disease.
- Weight Management: High-fiber foods are generally more filling, which can help control your appetite and prevent overeating. Additionally, fiber-rich foods often require more chewing, slowing down the eating process and giving your brain time to register feelings of fullness.
- Heart Health: Soluble fiber, found in foods like oats, legumes, and fruits, can help lower cholesterol levels by binding to dietary cholesterol and removing it from the body. By reducing cholesterol absorption, fiber helps protect against heart disease and stroke.
- Blood Sugar Control: Fiber slows down the absorption of sugar, preventing rapid spikes in blood glucose levels. This is especially beneficial for individuals with diabetes or prediabetes, as it helps regulate blood sugar levels and improves insulin sensitivity.
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases: Adequate fiber intake has been linked to a lower risk of developing various chronic diseases, including type 2 diabetes, certain types of cancer (such as colorectal cancer), and conditions like obesity and metabolic syndrome.
- Improved Gut Health: Fiber acts as a prebiotic, providing nourishment to the beneficial bacteria in your gut. These bacteria help maintain a healthy gut microbiome, which is essential for proper digestion, nutrient absorption, and a strong immune system.
Incorporating fiber into your diet is relatively easy. Begin by increasing your intake of whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts and seeds. Aim for a daily intake of 25-30 grams for women and 30-38 grams for men, but gradually increase your fiber intake to prevent any digestive discomfort.
Remember to drink plenty of water when consuming a high-fiber diet, as fiber absorbs water and helps soften the stool. With its numerous health benefits, fiber truly is a dietary superstar that should not be overlooked.
Promotes Digestive Health
Fiber is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in promoting digestive health. It aids in the proper functioning of the digestive system and helps prevent common digestive problems.
Here are some ways in which fiber benefits your digestive health:
- Prevents Constipation: One of the primary benefits of fiber is its ability to prevent and relieve constipation. It adds bulk to the stool, making it easier to pass through the intestines.
- Improves Bowel Movements: Consuming an adequate amount of fiber can regulate bowel movements and prevent both diarrhea and loose stools. It promotes regularity and reduces the risk of gastrointestinal disorders.
- Supports Healthy Gut Bacteria: Fiber acts as a prebiotic, providing nourishment to the beneficial bacteria in your gut. These bacteria help break down food, absorb nutrients, and support overall digestive health.
- Reduces the Risk of Diverticulitis: Diverticulitis is a condition characterized by inflamed pouches in the colon. A high-fiber diet can help prevent the development of these pouches and reduce the risk of diverticulitis.
- Manages Weight: Consuming fiber-rich foods can help manage weight by promoting a feeling of fullness and reducing hunger cravings. It can also help control blood sugar levels, which is beneficial for individuals with diabetes.
- Reduces the Risk of Colorectal Cancer: Studies have shown that a high-fiber diet is associated with a lower risk of colorectal cancer. Fiber helps keep the digestive system healthy and may prevent the development of cancerous cells.
To incorporate more fiber into your diet, include foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts. It is recommended to gradually increase your fiber intake to avoid digestive discomfort. Additionally, make sure to drink plenty of water to support the movement of fiber through your digestive system.
By adding fiber to your diet, you can improve your digestive health and enjoy the numerous benefits it offers. So start incorporating fiber-rich foods into your meals today and experience the fantastic impact it can have on your overall well-being.
Aids in Weight Management
Fiber plays a crucial role in promoting weight management and supporting overall health. Here’s how it can assist you in achieving your weight loss goals:
- Increased satiety: High-fiber foods tend to be more filling, which can help curb overeating and reduce calorie intake. When you consume foods rich in fiber, they expand in your stomach and promote a feeling of fullness, preventing excessive snacking or overindulgence.
- Reduced calorie absorption: Fiber-rich foods often require more chewing, which slows down the eating process. This delay allows your brain to receive signals from your stomach that you’re full, helping you avoid overeating. Additionally, soluble fiber can bind to dietary fat and cholesterol, preventing their absorption into the bloodstream.
- Stabilized blood sugar levels: Soluble fiber slows down the absorption of sugar, preventing rapid spikes in blood glucose levels. By regulating blood sugar, fiber helps control hunger and cravings, making it easier to manage your calorie intake.
- Improved gut health: Fiber acts as a prebiotic, providing nourishment for beneficial gut bacteria. A healthy gut microbiome is essential for proper digestion and nutrient absorption. When your gut is functioning optimally, it can impact your metabolism and overall weight management.
- Enhanced bowel regularity: Adequate fiber intake promotes regular bowel movements, preventing constipation and bloating. A healthy digestive system is essential for effective weight management as it allows for efficient elimination of waste products.
It’s important to note that increasing fiber intake should be done gradually, as a sudden significant increase can cause digestive discomfort. Aim to incorporate a variety of fiber-rich foods into your diet, such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts.
Remember, while fiber is beneficial for weight management, it is not a magic solution. To achieve and maintain a healthy weight, it’s important to combine a high-fiber diet with regular physical activity and a balanced eating plan.
– Reduces Cholesterol Levels
Fiber plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy cholesterol levels. It has been widely recognized as a dietary component that can effectively lower both total cholesterol and LDL (bad) cholesterol levels in the body.
Here’s how fiber helps in reducing cholesterol:
- Binds to cholesterol: Soluble fiber, found in foods like oats, beans, and fruits, forms a gel-like substance in the digestive system. This gel binds to cholesterol, preventing it from being absorbed into the bloodstream.
- Promotes excretion: Insoluble fiber, present in whole grains, nuts, and vegetables, adds bulk to the stool and helps in the regular elimination of waste products, including cholesterol. This prevents the reabsorption of cholesterol in the intestines.
- Reduces bile reabsorption: Fiber also interferes with the reabsorption of bile acids in the intestines. Bile is made from cholesterol, and when it is excreted, the liver needs to use more cholesterol to produce new bile. This process helps to lower cholesterol levels in the blood.
Several studies have shown the positive impact of fiber on cholesterol. For example, a review of 67 trials found that increasing fiber intake by just 7 grams per day resulted in a 7% reduction in total cholesterol and a 10% reduction in LDL cholesterol.
Additionally, soluble fiber has been shown to increase HDL (good) cholesterol levels, which further contributes to a healthier cholesterol profile.
To reap the cholesterol-lowering benefits of fiber, it’s important to consume a variety of high-fiber foods. Aim for at least 25-30 grams of fiber per day from sources such as whole grains, legumes, fruits, vegetables, and nuts.
However, it is important to note that while fiber can be beneficial for cholesterol management, it is not a substitute for a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle. It is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your diet or starting any new supplements.
Regulates Blood Sugar
Fiber plays a vital role in regulating blood sugar levels, making it an essential component of a healthy diet. Here’s how fiber helps to maintain stable blood sugar levels and prevent spikes and crashes:
- Slows down digestion: Soluble fiber, found in foods like oats, beans, and fruits, forms a gel-like substance when it comes into contact with water. This gel slows down the digestion process, resulting in a slower release of glucose into the bloodstream. This helps to prevent sudden spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Improves insulin sensitivity: Insoluble fiber, found in whole grains, nuts, and vegetables, helps the body become more responsive to insulin. This hormone is responsible for regulating blood sugar by allowing glucose to enter the cells where it can be used for energy. By improving insulin sensitivity, fiber helps to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Enhances satiety: High-fiber foods take longer to chew and digest, which can help you feel fuller for longer. This can prevent overeating and the consumption of sugary snacks that can lead to blood sugar spikes. Including fiber-rich foods in your meals and snacks can help regulate your appetite and prevent blood sugar imbalances.
- Reduces the glycemic index: The glycemic index (GI) measures how quickly carbohydrates in food raise blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GI cause a rapid increase in blood sugar, while those with a low GI result in a slower and more gradual rise. Fiber-rich foods, especially those with soluble fiber, can lower the glycemic index of a meal, making it a healthier choice for blood sugar control.
- Supports weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for blood sugar regulation. Fiber can aid in weight management by promoting feelings of fullness, reducing calorie intake, and supporting a healthy metabolism. By managing weight effectively, fiber helps to prevent insulin resistance and maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Adding more fiber to your diet through whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and seeds is a simple and effective way to regulate blood sugar levels. Aim to consume at least 25 grams of fiber per day for women and 38 grams for men to experience the blood sugar benefits that fiber provides.
Why Fiber is Fantastic for Your Health
Fiber is often overlooked when it comes to nutrition, but it is a dietary superstar that plays a crucial role in maintaining good health. This indigestible substance is found in plant-based foods and provides numerous benefits for your body.
Here are some reasons why fiber should be a key component of your diet:
- Improved Digestion: Fiber adds bulk to your stool, making it easier to pass through your digestive system. It helps prevent constipation and promotes regularity.
- Weight Management: High-fiber foods are typically more filling and can help control appetite. By including fiber-rich foods in your meals, you are less likely to overeat and can maintain a healthy weight.
- Heart Health: Soluble fiber, found in foods like oats and beans, can help lower cholesterol levels. This, in turn, reduces the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Blood Sugar Control: Fiber slows down the absorption of sugar into your bloodstream, preventing spikes in blood glucose levels. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing it.
- Colon Health: A high-fiber diet can lower the risk of colorectal cancer and other digestive disorders. It promotes healthy bowel movements and reduces the time waste spends in the colon, minimizing exposure to harmful substances.
It is recommended that adults consume between 25 to 30 grams of fiber per day. To increase your fiber intake, incorporate more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts into your diet. Start by making small changes like swapping refined grains for whole grains or adding a handful of berries to your breakfast cereal.
Remember to increase your fiber intake gradually and drink plenty of water to avoid digestive discomfort. By including fiber-rich foods in your daily meals, you can reap the amazing health benefits and take a step towards a healthier lifestyle.
Top Fiber-Rich Foods:
Fiber is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy digestive system and overall well-being. Incorporating fiber-rich foods into your diet can have numerous benefits, such as regulating blood sugar levels, promoting weight loss, and reducing the risk of heart disease. Here are some of the top fiber-rich foods you should consider adding to your meals:
- Whole Grains: Foods like oats, quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat bread are excellent sources of fiber. Opt for whole grain options whenever possible to increase your fiber intake.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are not only rich in fiber but also high in protein. These versatile legumes can be added to soups, salads, or main dishes for an extra boost of fiber.
- Fruits: Berries, apples, pears, and oranges are all packed with fiber. Incorporate these fruits into your diet as snacks or add them to smoothies and salads for a refreshing and fiber-rich treat.
- Vegetables: Broccoli, carrots, Brussels sprouts, and artichokes are just a few examples of fiber-rich vegetables. Including a variety of vegetables in your meals will not only provide fiber but also essential vitamins and minerals.
- Seeds: Chia seeds, flaxseeds, and hemp seeds are small but mighty when it comes to fiber content. Sprinkle them onto yogurt, oatmeal, or salads for an added crunch and fiber boost.
- Nuts: Almonds, pistachios, and walnuts are not only a great source of healthy fats but also provide a good amount of fiber. Enjoy a handful of nuts as a snack or incorporate them into your baking and cooking.
Remember, when increasing your fiber intake, it’s important to do so gradually and drink plenty of water to prevent digestive discomfort. Aim to include a variety of these fiber-rich foods in your diet to ensure you are getting a well-rounded intake of nutrients. By incorporating these foods into your meals, you’ll be well on your way to enjoying the benefits of a high-fiber diet.
Whole Grains and Cereals
Include whole grains and cereals in your diet to boost your fiber intake and reap the numerous health benefits associated with these foods. Whole grains and cereals are rich sources of dietary fiber, which is essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system and preventing various chronic diseases.
Here are some reasons why you should incorporate whole grains and cereals into your daily meals:
- High Fiber Content: Whole grains and cereals are excellent sources of dietary fiber. Fiber aids in digestion, helps regulate blood sugar levels, and promotes a feeling of fullness, which can aid in weight management.
- Heart Health: Consuming whole grains and cereals has been linked to a reduced risk of heart disease. The high fiber content helps lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of developing hypertension.
- Improved Digestion: The fiber in whole grains and cereals adds bulk to the stool, preventing constipation and promoting regular bowel movements. It also supports the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, leading to a healthy digestive system.
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases: Regular consumption of whole grains and cereals has been associated with a lower risk of developing chronic conditions such as type 2 diabetes, certain cancers, and obesity.
- Nutrient-Rich: Whole grains and cereals are packed with essential nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. They provide a good source of energy and help support overall well-being.
To incorporate more whole grains and cereals into your diet, opt for whole wheat bread, brown rice, oatmeal, quinoa, and whole grain cereals. Check food labels to ensure you’re choosing products that are made from whole grains rather than refined grains.
Remember to gradually increase your intake of whole grains and cereals to allow your body to adjust. Start by replacing refined grains with whole grains in your meals and snacks. Experiment with different recipes to make your meals more exciting and enjoyable.
In conclusion, whole grains and cereals are an essential part of a high-fiber diet. Including them in your meals can contribute to better digestion, heart health, and a reduced risk of chronic diseases. Start incorporating more whole grains and cereals into your diet today to reap the fantastic benefits of fiber.
Legumes and Beans
Legumes and beans are an excellent addition to your diet if you’re looking to increase your fiber intake. These plant-based foods are not only rich in fiber but also packed with essential nutrients. Incorporating legumes and beans into your meals can promote better digestion, weight management, and overall health.
Here are some reasons why legumes and beans should be on your grocery list:
- Fiber Powerhouse: Legumes and beans are known for their high fiber content. They provide a combination of soluble and insoluble fiber, which aids in maintaining bowel regularity and preventing constipation. Consuming these fiber-rich foods can also help lower cholesterol levels and improve heart health.
- Nutrient-Dense: Legumes and beans are a great source of plant-based protein, making them an excellent option for vegetarians and vegans. They are also packed with essential vitamins and minerals, including iron, folate, potassium, and magnesium. These nutrients play a crucial role in maintaining energy levels, supporting muscle function, and promoting overall well-being.
- Weight Management: Including legumes and beans in your diet can aid in weight management. The high fiber and protein content in these foods provide a sense of fullness, reducing the likelihood of overeating. They also have a low glycemic index, meaning they cause a slow and steady rise in blood sugar levels, keeping you satisfied for longer periods.
- Versatile and Delicious: Legumes and beans come in various forms, such as lentils, chickpeas, black beans, and kidney beans, offering a wide range of flavors and textures. They can be used in soups, salads, stews, and even desserts. Experimenting with different legume and bean recipes adds variety to your meals and makes healthy eating more enjoyable.
- Environmental Benefits: Legumes and beans are sustainable food choices. They require less water and produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to animal-based protein sources. Incorporating these plant-based foods into your diet can contribute to reducing your carbon footprint and promoting a more sustainable food system.
With so many benefits, it’s clear that legumes and beans are a dietary superstar when it comes to fiber intake. Try incorporating them into your meals and experience the positive impact they can have on your health and well-being.
Fruits and Vegetables
Incorporating a variety of fruits and vegetables into your diet is essential for reaping the benefits of fiber. Not only are they rich in fiber, but they also provide a wide range of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that contribute to overall health and well-being.
Here are some fiber-packed fruits and vegetables to include in your daily meals:
- Apples: With about 4 grams of fiber per medium-sized apple, this fruit is a great way to boost your daily fiber intake. Leave the skin on for maximum fiber content.
- Berries: Whether it’s strawberries, raspberries, blueberries, or blackberries, these tiny fruits are bursting with fiber. Enjoy them fresh, frozen, or added to smoothies.
- Avocado: This creamy fruit not only provides healthy fats but also contains around 6-7 grams of fiber per medium-sized avocado. Add slices to salads, sandwiches, or enjoy it as guacamole.
- Broccoli: Packed with fiber and essential nutrients, broccoli is a versatile vegetable that can be steamed, stir-fried, or added to soups and stews.
- Carrots: Crunchy and full of fiber, carrots are an excellent snack option. They can also be grated and added to salads or cooked as a side dish.
- Spinach: As a leafy green, spinach offers a good amount of fiber along with other beneficial compounds. Include it in salads, omelets, or sautéed as a side dish.
- Brussels sprouts: These mini cabbages are not only a great source of fiber but also provide vitamins and minerals. Roast them in the oven or sauté them for a tasty side dish.
Remember to aim for a variety of colors when choosing fruits and vegetables. Different colors indicate different types of antioxidants and nutrients, so incorporating a rainbow of produce into your diet ensures you’re getting a wide range of health benefits.
Additionally, opt for whole fruits and vegetables rather than juices to maximize your fiber intake. Juicing removes most of the fiber content, leaving behind mainly the natural sugars.
By including fiber-rich fruits and vegetables in your daily meals, you’ll not only support your digestive health but also reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Get creative and explore different recipes to make your fiber journey exciting and delicious!
Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds are not only delicious and versatile but also packed with fiber, making them an excellent addition to your diet. Incorporating nuts and seeds into your daily meals and snacks can provide numerous health benefits and help you meet your recommended fiber intake.
Here are some fiber-rich nuts and seeds to include in your diet:
- Almonds: These crunchy nuts are a great source of fiber, with about 3 grams of fiber per ounce. They are also rich in healthy fats, vitamin E, and antioxidants, making them a nutritious snack option.
- Chia Seeds: Chia seeds are tiny powerhouses of fiber, with approximately 5 grams of fiber per tablespoon. They are also packed with omega-3 fatty acids, protein, and various minerals. Add them to your smoothies, yogurt, or oatmeal for an extra fiber boost.
- Flaxseeds: Flaxseeds are high in fiber, containing around 2 grams of fiber per tablespoon. They are also a great source of omega-3 fatty acids and lignans, which have been linked to a reduced risk of heart disease and certain types of cancer. Sprinkle ground flaxseeds on your cereal or blend them into baked goods for added fiber content.
- Walnuts: These delicious nuts offer about 2 grams of fiber per ounce, along with a good amount of omega-3 fatty acids. Including walnuts in your diet can help improve heart health and may even have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Pumpkin Seeds: Pumpkin seeds are not only rich in fiber (approximately 1.7 grams of fiber per ounce) but also provide essential nutrients like magnesium, iron, and zinc. Enjoy them as a snack or sprinkle them over salads and soups.
By incorporating these fiber-packed nuts and seeds into your diet, you can promote healthy digestion, support heart health, and maintain a balanced diet. Remember to consume them in moderation as part of a well-rounded eating plan.
The Benefits of Adding Fiber to Your Diet
Fiber is often referred to as a dietary superstar, and for good reason. This indigestible carbohydrate is found in plant-based foods and provides numerous health benefits when incorporated into your daily diet.
Why should you consider adding more fiber to your meals? Here are some compelling reasons:
- Improved Digestive Health: Fiber adds bulk to your stool, preventing constipation and promoting regular bowel movements. It also acts as a prebiotic, nourishing the beneficial bacteria in your gut.
- Weight Management: High-fiber foods are generally low in calories and help you feel fuller for longer. By including fiber-rich options in your diet, you can curb your appetite and manage your weight more effectively.
- Heart Health: Soluble fiber can help lower cholesterol levels by binding to cholesterol in the digestive system and preventing its absorption into the bloodstream. This, in turn, reduces the risk of heart disease.
- Blood Sugar Control: Fiber slows down the absorption of sugar, preventing rapid spikes in blood glucose levels. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition.
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases: A fiber-rich diet has been associated with a lower risk of developing various chronic conditions, including type 2 diabetes, certain cancers, and diverticular disease.
So, how can you increase your fiber intake? Start by incorporating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts into your meals. Aim for at least 25-30 grams of fiber per day, gradually increasing your intake to avoid digestive discomfort.
Remember to drink plenty of water as you increase your fiber consumption, as this helps the fiber to work effectively in your digestive system.
Incorporating fiber into your diet is a simple and effective way to improve your overall health. Start making small changes today and experience the fantastic benefits of this dietary superstar!
Incorporating Fiber into Your Diet:
Fiber is an essential component of a healthy diet, providing a range of benefits for your digestive system, heart health, and overall well-being. However, many people struggle to consume enough fiber on a daily basis. Incorporating fiber-rich foods into your diet doesn’t have to be difficult. With a few simple changes, you can easily increase your fiber intake and reap the rewards of this dietary superstar.
Here are some easy ways to add more fiber to your meals:
- Choose whole grains: Opt for whole grain bread, pasta, and rice instead of their refined counterparts. Whole grains are a great source of fiber and provide more nutrients compared to processed grains.
- Load up on fruits and vegetables: Include a variety of fruits and vegetables in your meals. These natural fiber powerhouses not only contribute to your daily fiber intake but also provide a wide range of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Snack on nuts and seeds: Incorporate nuts and seeds into your snacks or sprinkle them on top of salads and yogurt. They are not only rich in fiber but also contain healthy fats and protein.
- Add legumes to your meals: Include beans, lentils, and chickpeas in your soups, stews, salads, and side dishes. Legumes are an excellent source of both soluble and insoluble fiber.
- Replace refined snacks with fiber-rich alternatives: Instead of reaching for processed snacks, opt for fiber-rich options like air-popped popcorn, whole fruit, or homemade energy bars made with oats and dried fruits.
- Include chia seeds and flaxseeds: These tiny seeds are packed with fiber and can be easily incorporated into your diet. Sprinkle them on cereals, yogurts, or add them to smoothies and baked goods.
Remember to increase your fiber intake gradually and drink plenty of water throughout the day. This helps prevent digestive discomfort and allows your body to adjust to the increased fiber consumption. Aim for the recommended daily intake of 25-30 grams for adult women and 30-38 grams for adult men.
By making these simple changes to your eating habits, you can easily incorporate more fiber into your diet. Enjoy the benefits of improved digestion, reduced risk of chronic diseases, and increased overall well-being that come with making fiber your new dietary superstar.
– Gradually Increase Intake
Introducing more fiber into your diet can be a game-changer for your overall health and well-being. However, it’s important to approach this change gradually. Adding too much fiber too quickly can lead to digestive discomfort, such as bloating, gas, and even diarrhea. To make the transition smoother, follow these tips:
- Start small: Begin by incorporating one high-fiber food into your meals or snacks each day. This could be as simple as adding a handful of raspberries to your breakfast or sprinkling chia seeds over your yogurt.
- Drink plenty of water: Fiber needs water to work effectively in your body. As you increase your fiber intake, make sure to hydrate properly by drinking enough water throughout the day. Aim for at least eight glasses of water daily.
- Listen to your body: Pay attention to how your body reacts to the increased fiber. If you experience any discomfort, slow down and give your body time to adjust. You can gradually increase the amount of fiber as your digestion becomes accustomed to it.
- Choose whole foods: Instead of relying on processed foods with added fiber, focus on incorporating whole foods. Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts are excellent sources of fiber and offer a wide range of other essential nutrients.
- Consult a healthcare professional: If you have any underlying health conditions or concerns, it’s always a good idea to consult your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian before making significant changes to your diet.
By gradually increasing your fiber intake, you can enjoy the benefits of this dietary superstar without any unwanted side effects. Remember, a healthy diet is all about balance, so be sure to include a variety of fiber-rich foods in your meals to maximize their nutritional benefits.
– Choose Whole Foods
When it comes to increasing your fiber intake, choosing whole foods is the way to go. Whole foods are minimally processed and contain all parts of the plant, including the bran, germ, and endosperm. These foods are rich in fiber and other essential nutrients, making them a fantastic addition to your diet.
Here are some tips on how to incorporate more whole foods into your daily meals:
- Opt for whole grains: Choose whole grain bread, brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat pasta instead of their refined counterparts. These whole grains contain more fiber and provide a steady release of energy throughout the day.
- Load up on fruits and vegetables: Fruits and vegetables are excellent sources of fiber. Aim to fill half your plate with a variety of colorful produce at each meal. Berries, apples, broccoli, and spinach are particularly high in fiber.
- Include legumes in your diet: Legumes such as lentils, chickpeas, and black beans are not only high in fiber but also rich in protein. Add them to soups, salads, or make vegetarian chili for a fiber-packed meal.
- Snack on nuts and seeds: Almonds, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are great sources of fiber. Enjoy a handful as a snack or sprinkle them on top of yogurt, oatmeal, or salads.
- Don’t forget about the skin: When possible, leave the skin on fruits and vegetables. The skin contains a significant amount of fiber, so it’s best to consume it to maximize your fiber intake.
By choosing whole foods, you not only increase your fiber intake but also improve your overall nutritional profile. These foods provide a range of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants essential for good health. Remember to gradually increase your fiber consumption and drink plenty of water to avoid digestive discomfort.
Experiment with New Recipes
Adding more fiber to your diet doesn’t mean you have to sacrifice taste or variety. In fact, it can be an exciting opportunity to explore different recipes and discover new flavors. Here are some ideas to help you experiment with new recipes that are packed with fiber:
- Start with whole grains: Replace refined grains like white bread and pasta with whole grain alternatives such as whole wheat, quinoa, brown rice, or oats. These ingredients can be used in a wide range of recipes, from salads to stir-fries to baked goods.
- Load up on fruits and vegetables: Incorporate a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables into your meals. They not only provide essential vitamins and minerals but also contribute to your daily fiber intake. Try new recipes that feature different types of produce, such as smoothies, stir-fries, or roasted vegetable medleys.
- Get creative with legumes: Legumes like beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent sources of fiber and can be used in various dishes. Experiment with recipes like bean salads, lentil soups, or chickpea curries. These plant-based proteins will not only increase your fiber intake but also add a delicious twist to your meals.
- Embrace the power of nuts and seeds: Nuts and seeds are not only rich in fiber but also provide healthy fats and protein. Add them to your salads, stir-fries, or homemade granola bars for an extra crunch and nutritional boost.
- Try new cooking methods: Explore different cooking techniques like grilling, steaming, roasting, or sautéing to enhance the flavors and textures of your dishes. These methods can bring out the natural sweetness of fruits and vegetables or add a smoky char to whole grains and legumes.
Remember to start slowly when introducing new recipes into your diet. Gradually incorporate fiber-rich foods and monitor how your body responds. Increasing your fiber intake too quickly can cause digestive discomfort. Stay hydrated and listen to your body’s signals.
By experimenting with new recipes, you can make your fiber-rich diet exciting and enjoyable. Don’t be afraid to step out of your comfort zone and explore the wide range of delicious options available. Your taste buds and your gut will thank you!
– Stay Hydrated
When it comes to optimizing your fiber intake, staying hydrated is essential. Fiber absorbs water and expands in your digestive system, helping to keep everything moving smoothly. Without enough water, fiber can become dry and cause discomfort or constipation. Here are some tips to ensure you stay hydrated while increasing your fiber intake:
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Aim for at least eight glasses or two liters.
- Include hydrating foods in your diet, such as fruits and vegetables with high water content like watermelon, cucumbers, and oranges.
- Avoid excessive consumption of dehydrating beverages like caffeinated drinks, alcohol, and sugary sodas.
- Consider drinking herbal teas or infusing water with fresh fruits or herbs for added flavor.
- Keep a water bottle with you at all times as a reminder to stay hydrated.
- Start your day with a glass of water and make it a habit to drink water before each meal.
- Listen to your body’s thirst cues and drink water whenever you feel thirsty.
Remember, fiber works best when there is enough water available to help it move smoothly through your digestive system. By staying hydrated, you can ensure that your body reaps all the benefits of a fiber-rich diet, such as improved digestion, reduced risk of chronic diseases, and increased satiety.
The Importance of Fiber in Your Diet
Fiber is often overlooked when it comes to discussing a healthy diet, yet it plays a crucial role in maintaining overall well-being. This indigestible substance found in plant-based foods provides a range of health benefits that can significantly improve your quality of life.
Here are some reasons why fiber should become your new dietary superstar:
- Promotes Digestive Health: Fiber adds bulk to your stool, helping to prevent constipation and promote regular bowel movements. It also acts as a natural laxative, reducing the risk of developing conditions such as hemorrhoids and diverticulitis.
- Controls Blood Sugar Levels: Soluble fiber found in foods like oats, legumes, and fruits slows down the absorption of sugar, preventing spikes in blood glucose levels. This can be especially beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the disease.
- Manages Weight: High-fiber foods are typically more filling and lower in calories, making them a great addition to weight management plans. By increasing satiety, fiber helps control appetite and reduce overall calorie intake.
- Reduces Cholesterol: Soluble fiber also helps lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels by binding to cholesterol in the digestive system and preventing its absorption into the bloodstream. This, in turn, reduces the risk of heart disease.
- Promotes a Healthy Gut Microbiome: Fiber acts as a prebiotic, providing nourishment for beneficial gut bacteria. A healthy gut microbiome is essential for optimal digestion, nutrient absorption, and a strong immune system.
Now that you understand the importance of fiber, it’s time to incorporate more of it into your diet. Aim for at least 25-30 grams of fiber per day from a variety of sources such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts. Remember to increase your fiber intake gradually and drink plenty of water to prevent any digestive discomfort.
Make fiber your dietary superstar and reap the incredible health benefits it has to offer!
Fiber and Gut Health:
Fiber is often referred to as the unsung hero of a healthy diet. It plays a crucial role in maintaining gut health and overall well-being. The human digestive system is home to trillions of bacteria, collectively known as the gut microbiota. These bacteria help break down food, produce essential nutrients, and support various aspects of our health. Consuming an adequate amount of fiber is essential for keeping this intricate ecosystem in balance.
Here are some key ways in which fiber promotes gut health:
- Improved digestion: Fiber adds bulk to the diet, helping to prevent constipation and promote regular bowel movements. It acts as a natural laxative, keeping things moving smoothly through the digestive tract.
- Feeding beneficial bacteria: Certain types of fiber, known as prebiotics, serve as food for beneficial bacteria in the gut. These bacteria ferment prebiotic fiber and produce short-chain fatty acids, which provide energy to the cells lining the colon and promote a healthy gut environment.
- Reduced inflammation: A high-fiber diet has been linked to lower levels of inflammation in the body. By supporting a diverse and healthy gut microbiota, fiber helps regulate the immune system and reduce the risk of chronic inflammation, which is associated with various diseases.
- Weight management: Fiber-rich foods are often more filling and can help control appetite, leading to better weight management. Additionally, fiber slows down the absorption of nutrients, helping to stabilize blood sugar levels and prevent sudden spikes and crashes.
- Lowered risk of chronic diseases: Adequate fiber intake has been associated with a reduced risk of various chronic diseases, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. It may also help lower cholesterol levels and improve blood pressure.
To reap the benefits of fiber for gut health, it’s important to consume a variety of fiber-rich foods. Good sources of fiber include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and seeds. Aim to gradually increase your fiber intake and drink plenty of water to help prevent any potential digestive discomfort.
In conclusion, fiber is a dietary superstar when it comes to gut health. By supporting digestion, nourishing beneficial bacteria, reducing inflammation, aiding in weight management, and lowering the risk of chronic diseases, fiber plays a crucial role in maintaining overall well-being. Make sure to include fiber-rich foods in your daily diet to support a healthy gut and enjoy the numerous benefits it provides.
– Supports Healthy Gut Bacteria
Fiber is not only beneficial for your digestive system, but it also plays a crucial role in supporting the growth and maintenance of healthy gut bacteria. These bacteria, known as gut microbiota, are essential for overall gut health and play a significant role in various bodily functions.
Here are some ways in which fiber supports the growth of healthy gut bacteria:
- Prebiotic Effect: Certain types of fiber, known as prebiotics, act as food for the beneficial bacteria in your gut. They pass through the small intestine undigested and reach the colon, where they are fermented by the gut microbiota. This fermentation process produces short-chain fatty acids, such as butyrate, which provide nourishment to the cells lining your colon and promote a healthy gut environment.
- Diversity of Gut Microbiota: Consuming a variety of fiber-rich foods helps to increase the diversity of gut microbiota. Different types of fiber feed different types of bacteria, resulting in a more balanced and diverse gut microbiome. A diverse gut microbiome is associated with better overall health and a lower risk of various diseases.
- Enhanced Digestive Function: Fiber helps to regulate bowel movements and prevent constipation by adding bulk to the stool. This promotes regular bowel movements and prevents the buildup of harmful bacteria in the colon. Additionally, fiber can help alleviate symptoms of certain digestive disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
- Immune System Support: The gut microbiota plays a vital role in supporting a healthy immune system. Fiber helps to stimulate the growth of beneficial bacteria that contribute to a robust immune response. A healthy gut microbiome helps to regulate immune function, reducing the risk of autoimmune conditions and promoting overall immune system health.
Incorporating a variety of fiber-rich foods into your diet, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts, can help support the growth of healthy gut bacteria. Aim to consume at least 25-30 grams of fiber per day for optimal gut health and overall well-being.
– Prevents Constipation
Fiber is a crucial component of a healthy diet, and one of its most important benefits is its ability to prevent constipation. Constipation is a common digestive problem characterized by infrequent bowel movements or difficulty passing stool. It can leave you feeling uncomfortable, bloated, and sluggish. However, with the inclusion of fiber-rich foods in your diet, you can effectively prevent and alleviate constipation.
Here are some ways in which fiber helps in preventing constipation:
- Increases stool bulk: Fiber adds bulk to the stool, making it easier to pass through the digestive system. This helps to promote regular bowel movements and prevents the stool from becoming hard and dry.
- Improves bowel regularity: Fiber acts as a natural laxative, stimulating the muscles in the intestines and promoting regular bowel movements. It helps to regulate the transit time of food through the digestive system, preventing constipation.
- Softens the stool: Soluble fiber absorbs water and forms a gel-like substance in the intestines. This softens the stool, making it easier to pass through the colon and reducing the chances of constipation.
- Provides prebiotic effects: Certain types of fiber, known as prebiotics, act as food for the beneficial bacteria in the gut. These bacteria help to maintain a healthy digestive system and promote regular bowel movements.
To prevent constipation, it is recommended to consume a variety of fiber-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts. Aim to gradually increase your fiber intake to allow your body to adjust. Additionally, ensure you drink plenty of water throughout the day to help the fiber work effectively.
While fiber is beneficial for preventing constipation, it is important to note that excessive fiber intake without adequate fluid intake can have the opposite effect and lead to bloating and discomfort. It is crucial to maintain a balance and listen to your body’s needs.
In conclusion, incorporating fiber into your diet is a fantastic way to prevent constipation. By increasing stool bulk, improving bowel regularity, softening the stool, and providing prebiotic effects, fiber ensures a healthy digestive system and regular bowel movements. Start making fiber a dietary superstar in your life and enjoy the benefits it offers!
– Reduces the Risk of Colon Cancer
One of the most significant health benefits of consuming a high-fiber diet is its ability to reduce the risk of colon cancer. Colon cancer is a prevalent and potentially fatal disease that affects thousands of people each year. However, studies have shown that incorporating fiber-rich foods into your daily diet can significantly lower the risk of developing this type of cancer.
Fiber plays a crucial role in promoting a healthy digestive system, and this includes reducing the risk of colon cancer. Soluble fiber, found in foods such as oats, barley, and legumes, helps to soften the stool and promote regular bowel movements. This helps to prevent the build-up of waste and toxins in the colon, reducing the risk of cancerous cells forming.
In addition, insoluble fiber, which is found in foods like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, adds bulk to the stool and speeds up its passage through the digestive tract. This helps to prevent constipation and reduces the time that waste spends in the colon. By minimizing the contact between waste and the colon walls, insoluble fiber reduces the risk of harmful substances causing damage and inflammation, which can lead to the development of cancer cells.
Furthermore, fiber acts as a prebiotic, providing nourishment for the beneficial bacteria in the gut. These bacteria play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy colon by producing short-chain fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties. By promoting the growth of these beneficial bacteria, fiber helps to create an environment in the colon that is less favorable for the growth of cancer cells.
To incorporate more fiber into your diet and reduce the risk of colon cancer, consider including the following high-fiber foods:
- Whole grains: oats, brown rice, quinoa
- Fruits: apples, bananas, berries
- Vegetables: broccoli, carrots, leafy greens
- Legumes: beans, lentils, chickpeas
- Nuts and seeds: almonds, chia seeds, flaxseeds
It is important to gradually increase your fiber intake and drink plenty of water to aid digestion. Start by introducing one or two high-fiber foods into your diet and gradually increase the portion sizes over time.
In conclusion, consuming a high-fiber diet can significantly reduce the risk of colon cancer. By promoting regular bowel movements, preventing constipation, and nourishing beneficial gut bacteria, fiber plays a vital role in maintaining a healthy colon. So, make fiber your new dietary superstar and enjoy the numerous health benefits it offers.
Improves Overall Digestion
Fiber is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in improving overall digestion. It acts as a natural cleanser for your digestive system, keeping it healthy and functioning optimally. Here’s how fiber works its magic:
- Prevents Constipation: One of the key benefits of fiber is its ability to prevent and relieve constipation. It adds bulk to your stool, making it easier to pass through the intestines. This helps promote regular bowel movements and prevents the discomfort and pain associated with constipation.
- Promotes Healthy Gut Bacteria: Fiber acts as a prebiotic, providing nourishment to the beneficial bacteria in your gut. These bacteria help break down food particles, produce essential vitamins, and support the absorption of nutrients. By promoting a healthy gut microbiome, fiber enhances digestion and improves overall gut health.
- Enhances Nutrient Absorption: When you consume fiber-rich foods, it slows down the digestion process. This allows for better absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. Fiber also helps regulate blood sugar levels, preventing spikes and crashes that can negatively impact digestion.
- Reduces the Risk of Digestive Disorders: A diet high in fiber has been linked to a decreased risk of various digestive disorders, including diverticulosis, hemorrhoids, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Fiber helps maintain regularity, reduces inflammation, and supports a healthy digestive system.
- Provides Satiety and Weight Management: High-fiber foods tend to be more filling and satisfying. They take longer to digest, keeping you feeling fuller for longer periods. This can aid in weight management by reducing overeating and snacking between meals.
It’s important to note that increasing fiber intake should be done gradually to avoid digestive discomfort. Aim to consume a variety of fiber-rich foods, such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts. Additionally, drink plenty of water to help fiber move through your digestive system smoothly.
By incorporating fiber into your diet, you can improve overall digestion, support gut health, and reduce the risk of digestive disorders. So go ahead and make fiber your new dietary superstar!
Fiber: Your New Dietary Superstar
Fiber is often overlooked when it comes to nutrition, but it is a crucial component of a healthy and balanced diet. This dietary superstar not only aids in digestion but also offers a range of other health benefits. Here’s why fiber should become your new best friend in the kitchen:
- Fiber promotes digestive health: It adds bulk to your stool, making it easier to pass through your digestive system, preventing constipation and promoting regular bowel movements.
- Weight management: High-fiber foods keep you feeling fuller for longer, reducing the chances of overeating and aiding in weight management. They require more chewing, which slows down the eating process and gives your brain time to register that you’re full.
- Heart health: Fiber-rich foods, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, have been linked to a lower risk of heart disease. They help to reduce cholesterol levels, maintain healthy blood pressure, and improve overall heart function.
- Diabetes control: Fiber slows down the absorption of sugar, preventing blood sugar spikes after meals. This can help manage diabetes and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Lower risk of certain cancers: A high-fiber diet has been associated with a reduced risk of colorectal cancer. Fiber helps keep the digestive system healthy and prevents the formation of cancer-causing compounds.
- Improved gut health: Fiber acts as a prebiotic, providing fuel for the beneficial bacteria in your gut. These bacteria play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy immune system and preventing digestive disorders.
- Healthy skin: By promoting regular bowel movements and reducing toxins in the body, fiber contributes to clearer and healthier skin.
To increase your fiber intake, incorporate more whole foods into your diet. Choose whole grains, such as oats, brown rice, and quinoa, over refined grains. Include a variety of fruits and vegetables in your meals, and opt for legumes, nuts, and seeds as snacks. Aim for at least 25-30 grams of fiber per day, gradually increasing your intake to avoid digestive discomfort.
Remember to drink plenty of water when increasing your fiber intake to help it move smoothly through your system. Start making fiber a priority in your diet today, and enjoy the numerous benefits it can offer for your overall health and well-being.
Tips for a Fiber-Rich Lifestyle:
Incorporating more fiber into your diet is a great way to improve your health and well-being. Here are some tips to help you embrace a fiber-rich lifestyle:
- Choose whole grains: Opt for whole grain bread, pasta, and rice instead of their refined counterparts. Whole grains are packed with fiber, providing more nutrients and promoting better digestion.
- Load up on fruits and vegetables: Make it a goal to include a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables in your meals. These natural foods are not only rich in fiber but also contain essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Snack on nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are excellent sources of dietary fiber. Keep a handful of these nutritious snacks on hand for a quick and convenient fiber boost.
- Don’t forget legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are not only affordable but also high in fiber. Incorporate them into soups, stews, salads, or as a side dish to increase your daily fiber intake.
- Include fiber-rich snacks: Instead of reaching for processed snacks, opt for fiber-rich alternatives. Fresh fruits, raw vegetables with hummus, or a handful of whole grain crackers with nut butter are all great options.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking an adequate amount of water is essential for proper digestion and maximizing the benefits of fiber. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water per day to keep your digestive system running smoothly.
- Gradually increase fiber intake: It’s important to increase your fiber intake gradually to avoid digestive discomfort. Start by adding small portions of fiber-rich foods to your meals and gradually increase the amount over time.
- Read food labels: When grocery shopping, take the time to read food labels and choose products that are high in fiber. Look for items with at least 3 grams of fiber per serving to ensure you’re getting the most out of your food choices.
- Stay consistent: Consistency is key when it comes to maintaining a fiber-rich lifestyle. Make it a habit to include fiber-rich foods in your meals and snacks daily to experience the long-term benefits of improved digestion and overall health.
By following these tips, you can easily incorporate more fiber into your diet and reap the numerous benefits it offers. Remember, a fiber-rich lifestyle can lead to better digestive health, increased energy levels, and improved overall well-being.
Read Food Labels
When it comes to incorporating more fiber into your diet, one of the most important steps is to read food labels. Food labels provide valuable information about the nutritional content of the products we consume, including the amount of fiber they contain. By paying attention to these labels, you can make more informed choices and ensure you’re getting enough fiber in your diet.
Here are some tips for effectively reading food labels:
- Check the serving size: Food labels provide information based on a specific serving size. Make sure to adjust the values according to the amount you plan to consume.
- Look for total fiber content: Find the section that lists the amount of dietary fiber per serving. Aim for products that contain at least 3 grams of fiber per serving.
- Check the ingredients list: In addition to the total fiber content, it’s important to see what the source of fiber is. Look for whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes, as these are often rich in fiber.
- Beware of misleading claims: Food manufacturers often use marketing tactics to make their products appear healthier than they really are. Be cautious of terms such as “high fiber” or “good source of fiber” without actually checking the specific fiber content.
- Compare different products: If you have multiple options for a specific food item, compare the fiber content and choose the one with higher fiber.
- Consider the overall nutritional value: While fiber is important, it’s also essential to look at the overall nutritional profile of the product. Ensure that it aligns with your dietary goals and preferences.
By practicing these habits, you can become more proficient at reading food labels and making choices that support your fiber intake. Remember that increasing your fiber consumption is a gradual process, so be patient with yourself as you make dietary changes. Over time, you’ll reap the benefits of a fiber-rich diet, including improved digestion, weight management, and lower risk of chronic diseases.
– Plan Balanced Meals
Eating a diet rich in fiber doesn’t mean you have to sacrifice taste or variety. By planning balanced meals, you can easily incorporate fiber-rich foods into your daily routine. Here are some tips to help you create well-rounded meals that are packed with fiber:
- Include fruits and vegetables: Make sure to include a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables in your meals. These are excellent sources of fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Aim for at least five servings per day.
- Incorporate whole grains: Opt for whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, whole wheat bread, and oats. These are high in fiber and provide sustained energy throughout the day.
- Add legumes and beans: Legumes and beans, such as lentils, chickpeas, and black beans, are not only rich in fiber but also a great source of plant-based protein. Consider adding them to salads, soups, or as a side dish.
- Choose lean proteins: Include lean proteins like chicken, fish, tofu, or eggs in your meals. These foods provide essential nutrients while keeping your meals balanced.
- Don’t forget healthy fats: Incorporate healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. These fats are important for overall health and can help improve nutrient absorption.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Fiber needs water to move through the digestive system smoothly and prevent constipation.
Remember to plan your meals ahead of time and make a grocery list to ensure you have all the necessary ingredients on hand. It’s also a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to customize a meal plan that meets your specific dietary needs.
By following these guidelines, you can easily incorporate fiber-rich foods into your meals, promoting a healthier digestive system and overall well-being.
– Snack on Fiber-Rich Foods
Incorporating fiber-rich snacks into your daily diet is a great way to increase your overall fiber intake. These snacks not only keep you feeling full and satisfied but also provide numerous health benefits. Here are some delicious and nutritious fiber-rich snack ideas:
- Fresh fruits: Snacking on fresh fruits like apples, pears, berries, and oranges is an excellent way to boost your fiber intake. These fruits are not only rich in fiber but also packed with essential vitamins and antioxidants.
- Vegetable sticks: Crunchy vegetables like carrots, celery, and bell peppers are not only low in calories but also high in fiber. Pair them with a tasty hummus or yogurt dip for added flavor.
- Whole grain crackers: Opt for whole grain crackers instead of refined ones. These crackers are usually made from whole wheat or other whole grains, providing a good amount of fiber. Pair them with some cheese or nut butter for a satisfying snack.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are all excellent sources of fiber. They are also packed with healthy fats and protein, making them a perfect snack to keep you energized throughout the day.
- Popcorn: Air-popped popcorn is a great option for a low-calorie, high-fiber snack. It is a whole grain and provides a satisfying crunch. Just be mindful of added butter or salt, as it can increase the calorie content.
- Greek yogurt: Greek yogurt is not only a good source of protein but also contains a decent amount of fiber. Choose plain, unsweetened yogurt and add some fresh fruits or a sprinkle of granola for extra flavor and fiber.
Remember to stay hydrated and drink plenty of water when increasing your fiber intake. Fiber absorbs water, so it is essential to drink fluids to ensure proper digestion and prevent any discomfort.
Snacking on fiber-rich foods can help regulate your digestion, promote satiety, and support overall gut health. Aim to incorporate these snacks into your daily routine to reap the many benefits of a fiber-rich diet.
Stay Consistent and Patient
When it comes to incorporating more fiber into your diet, staying consistent and patient is key. Here are some tips to help you on your journey:
- Start slow: Introducing too much fiber into your diet too quickly can cause digestive discomfort. Gradually increase your fiber intake over time to allow your body to adjust.
- Choose whole foods: Opt for whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts instead of processed foods that are often low in fiber. These natural sources of fiber are also packed with other essential nutrients that promote overall health.
- Stay hydrated: Fiber absorbs water, so it’s important to drink plenty of fluids to help prevent constipation. Aim for at least eight glasses of water per day.
- Plan your meals: Incorporate high-fiber foods into your meals and snacks. Plan ahead to ensure you have a variety of fiber-rich options available, such as adding berries to your breakfast or swapping white rice with quinoa for dinner.
- Monitor your progress: Keep track of your fiber intake and monitor how it makes you feel. Pay attention to any changes in your digestion or energy levels. Adjust your fiber intake as needed to find the right balance for your body.
- Seek support: If you’re struggling to incorporate more fiber into your diet, don’t hesitate to seek support. Consult a registered dietitian or join a community of individuals with similar dietary goals for tips, guidance, and motivation.
Remember, increasing your fiber intake is a lifestyle change that takes time. Be patient with yourself and celebrate small victories along the way. Over time, you will start to notice the positive effects of a fiber-rich diet, such as improved digestion, increased satiety, and better overall health.