Gastritis Relief: Diet Changes and Treatment
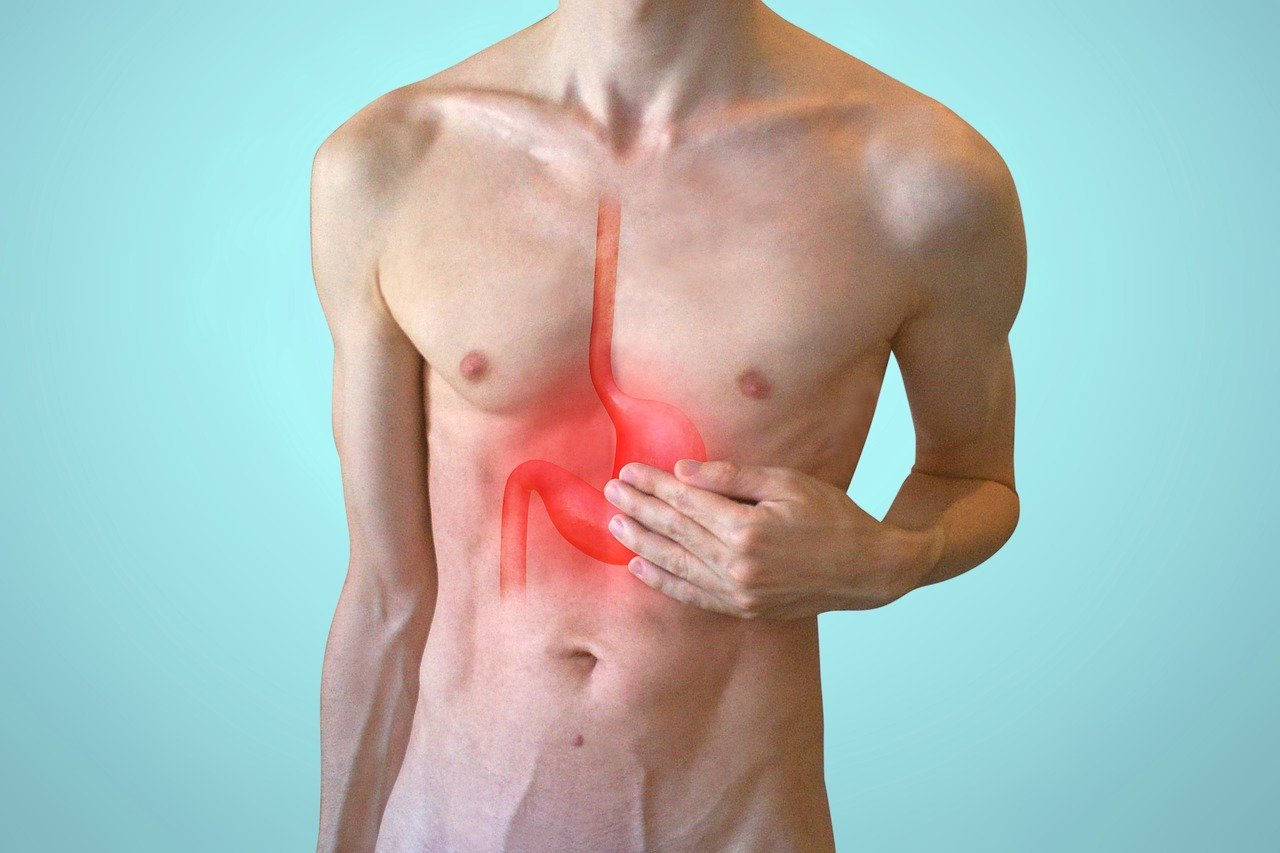
Table of Contents
Understanding Gastritis: Causes and Symptoms
Gastritis is a condition that occurs when the lining of the stomach becomes inflamed or swollen. It can be acute, which means it appears suddenly and lasts for a short period, or chronic, which means it persists for a long time. Gastritis can cause various symptoms and discomfort, but with the right diet changes and treatment, relief is possible.
Causes of Gastritis:
- Infection: The most common cause of gastritis is an infection caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori). This bacterium can live in the stomach and cause inflammation.
- Medications: Prolonged use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin or ibuprofen can irritate the stomach lining and lead to gastritis.
- Alcohol and Smoking: Excessive alcohol consumption and smoking can weaken the stomach lining, making it more susceptible to inflammation.
- Stress: Severe stress or trauma can disrupt the protective mechanisms of the stomach and contribute to the development of gastritis.
- Autoimmune Disorders: In some cases, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the cells of the stomach lining, leading to gastritis.
Symptoms of Gastritis:
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Feeling of fullness after eating
- Bloating and belching
- Indigestion
- Black or tarry stools
- Vomiting blood or coffee ground-like material
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. They may perform tests such as blood tests, stool tests, or endoscopy to determine the cause and severity of your gastritis.
Treating Gastritis:
The treatment for gastritis depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In many cases, lifestyle changes and dietary modifications can provide relief. These include:
- Avoiding foods and beverages that irritate the stomach, such as spicy foods, caffeine, alcohol, and acidic foods
- Eating smaller, more frequent meals to reduce the workload on the stomach
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, or counseling
- Taking medications prescribed by your healthcare professional, such as proton pump inhibitors or antibiotics to eradicate H. pylori infection
- Stopping the use of NSAIDs, if possible, or using them under medical supervision
It is essential to follow your healthcare professional’s advice and treatment plan to manage gastritis effectively. In some cases, additional medical interventions may be necessary, such as endoscopic procedures or surgery, depending on the severity and complications of the condition.
By understanding the causes and symptoms of gastritis and implementing the necessary diet changes and treatment, relief from the discomfort and inflammation associated with gastritis can be achieved.
The Role of Diet in Gastritis Management
Gastritis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the stomach lining. It can be caused by various factors such as bacterial infections, excessive alcohol consumption, prolonged use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and certain autoimmune disorders. While medication and lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing gastritis, diet also plays a significant role in providing relief and promoting healing.
Here are some dietary changes that can help manage gastritis:
- Avoid Trigger Foods: Certain foods can trigger or worsen gastritis symptoms. These may include spicy foods, acidic foods and beverages, fried and fatty foods, and caffeine. It is important to identify and avoid these trigger foods to prevent inflammation and irritation of the stomach lining.
- Include Anti-inflammatory Foods: Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods in your diet can help reduce inflammation in the stomach. Some examples of anti-inflammatory foods include fatty fish (such as salmon and mackerel), leafy greens, ginger, turmeric, berries, and olive oil.
- Opt for a Low-Fat Diet: Consuming a low-fat diet can help ease symptoms of gastritis. High-fat foods can increase stomach acid production and delay stomach emptying, leading to more irritation and discomfort. Choose lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables while limiting the intake of fatty meats, fried foods, and full-fat dairy products.
- Eat Regular, Small Meals: Instead of having large meals, opt for smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day. This can help reduce the burden on the digestive system and prevent excessive stomach acid production.
- Avoid Alcohol and Smoking: Both alcohol and smoking can irritate the stomach lining and worsen gastritis symptoms. It is crucial to avoid or limit alcohol consumption and quit smoking to promote healing and prevent further damage.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking an adequate amount of water can help dilute stomach acid and reduce irritation. Aim to drink at least 8 cups of water per day, and avoid carbonated and caffeinated beverages.
While these dietary changes can provide relief and promote healing in gastritis, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized advice and guidance. They can help create a tailored diet plan based on your specific needs and underlying causes of gastritis.
Foods to Avoid to Reduce Gastritis Symptoms
Gastritis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the stomach lining. It can cause discomfort and pain, and certain foods can exacerbate these symptoms. Making dietary changes and avoiding certain foods can help reduce gastritis symptoms. Here are some foods to avoid:
- Spicy Foods: Spices such as chili powder, black pepper, and hot sauce can irritate the stomach lining, leading to increased inflammation and discomfort. It’s best to avoid these spicy foods if you have gastritis.
- Acidic Foods: Citrus fruits, tomatoes, and their juices are highly acidic and can worsen gastritis symptoms. These foods can increase the production of stomach acid, leading to increased irritation and inflammation. Limit or avoid consuming these acidic foods.
- Fried and Fatty Foods: Fried and fatty foods can be difficult to digest and can cause the stomach to produce more acid, leading to increased discomfort. Avoid foods such as French fries, deep-fried snacks, and fatty cuts of meat.
- Caffeine and Alcohol: Caffeinated beverages like coffee and tea, as well as alcoholic drinks, can irritate the stomach lining. These substances can increase acid production and worsen gastritis symptoms. Opt for decaffeinated beverages and limit alcohol consumption.
- Processed and Spicy Meats: Processed meats such as sausages, hot dogs, and bacon contain high levels of preservatives and spices, which can aggravate gastritis. It’s best to opt for lean, unprocessed meats and avoid heavily seasoned options.
- Carbonated Drinks: Carbonated drinks like soda can cause bloating and increase stomach acid production, leading to discomfort. Avoid carbonated beverages and opt for water or herbal tea instead.
Remember, everyone’s tolerance for certain foods may vary, so it’s essential to pay attention to your body and how it reacts to different foods. Keeping a food diary can help identify trigger foods that worsen your gastritis symptoms. By making these dietary changes and avoiding foods that irritate your stomach lining, you can help alleviate gastritis symptoms and promote better digestive health.
Beneficial Foods for Gastritis Relief
Gastritis, an inflammation of the stomach lining, can cause discomfort and pain. While certain medications and treatments can help alleviate symptoms, making dietary changes can also play a significant role in providing relief. Incorporating these beneficial foods into your diet may help soothe your gastritis symptoms:
- High-fiber foods: Foods rich in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help regulate digestion and prevent constipation, a common symptom of gastritis.
- Probiotic-rich foods: Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that promote a healthy gut. Consuming foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi can help restore the balance of your gut flora, reducing inflammation.
- Lean proteins: Opt for lean meats, such as skinless poultry and fish, as they are easier to digest and less likely to irritate the stomach lining. Avoid fried or fatty meats, which can worsen symptoms.
- Ginger: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, ginger can help reduce inflammation in the stomach. Consider incorporating fresh ginger into your meals or drinking ginger tea.
- Green leafy vegetables: Vegetables like kale, spinach, and broccoli are rich in antioxidants and can help protect the stomach lining. Include these nutritious greens in your meals to support gastric health.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Foods like salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds contain omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory effects. These healthy fats can help reduce inflammation in the stomach and alleviate gastritis symptoms.
Remember, everyone’s body is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. It’s essential to listen to your body and pay attention to any food triggers that may worsen your symptoms. If you experience severe or persistent symptoms, consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Medical Treatment Options for Gastritis
While making dietary changes is an essential part of managing gastritis, there are also medical treatment options available to provide relief from symptoms and promote healing. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment plan for your specific condition. Here are some common medical treatment options for gastritis:
- Antacids: Over-the-counter antacids can help neutralize stomach acid and provide temporary relief from gastritis symptoms. They are available in various forms such as tablets, liquids, or chewable tablets.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): PPIs are medications that reduce the production of stomach acid. They are often prescribed for more severe cases of gastritis or when symptoms persist despite dietary changes. PPIs are available both over-the-counter and in stronger prescription forms.
- H2 Blockers: H2 blockers are another type of medication that reduces the production of stomach acid. They can help relieve symptoms and promote healing in the stomach lining. Like PPIs, H2 blockers are available over-the-counter and in prescription strength.
- Antibiotics: If gastritis is caused by an infection, such as H. pylori bacteria, antibiotics may be prescribed to eliminate the infection and promote healing. It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by the healthcare professional.
- Medications to protect the stomach lining: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help protect the stomach lining from further damage. These medications may include sucralfate or prostaglandin analogs.
- Medications to manage pain: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen, can help alleviate discomfort associated with gastritis. However, it is important to avoid nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or aspirin, as they can worsen gastritis symptoms and irritate the stomach lining.
Remember, while medical treatment options can provide relief, they should be used in conjunction with dietary changes and lifestyle modifications for optimal management of gastritis. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new medication or treatment regimen.